Note: On some ISO shelters, some of the primary structural components may be concealed within the wall, roof, and floor panels. The areas where the adjacent panels join will be thoroughly inspected. This inspection will meet the criteria for the Wall Beams and the Roof Beams
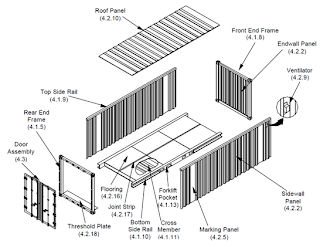
- 4.1.1 Corner Fitting. Internationally standard fitting (casting) located at the eight corners of the container structure to provide means of handling, stacking and securing containers. Specifications are defined in ISO 1161.
- 4.1.2 Corner Post. Vertical structural member located at the four corners of the container and to which the corner fittings are joined.
- 4.1.3 Door Header. Lateral structural member situated over the door opening and joined to the corner fittings in the door end frame.
- 4.1.4 Door Sill. Lateral structural member at the bottom of the door opening and joined to the corner fittings in the door end frame.
- 4.1.5 Rear End Frame. The structural assembly at the rear (door end) of the container consisting of the door sill and header joined at the rear corner fittings to the rear corner posts to form the door opening.
- 4.1.6 Top End Rail. Lateral structural member situated at the top edge of the front end (opposite the door end) of the container and joined to the corner fittings.
- 4.1.7 Bottom End Rail. Lateral structural member situated at the bottom edge of the front end (opposite the door end) of the container and joined to the corner fittings.
- 4.1.8 Front End Frame. The structural assembly at the front end (opposite the door end) of the container consisting of top and bottom end rails joined at the front corner fittings to the front corner posts.
- 4.1.9 Top Side Rail. Longitudinal structural member situated at the top edge of each side of the container and joined to the corner fittings of the end frames.
- 4.1.10 Bottom Side Rail. Longitudinal structural member situated at the bottom edge of each side of the container and joined to the corner fittings to form a part of the understructure.
- 4.1.11 Cross Member. Lateral structural member attached to the bottom side rails that supports the
- flooring.
- 4.1.12 Understructure. An assembly consisting of bottom side and end rails, door sill (when applicable), cross members and forklift pockets.
- 4.1.13 Forklift Pocket. Reinforced tunnel (installed in pairs) situated transversely across the understructure and providing openings in the bottom side rails at ISO prescribed positions to enable either empty capacity or empty and loaded capacity container handling by forklift equipment.
- 4.1.14 Forklift Pocket Strap. The plate welded to the bottom of each forklift pocket opening or part of bottom siderail. The forklift pocket strap is a component of the forklift pocket.
- 4.1.15 Gooseneck Tunnel. Recessed area in the forward portion of the understructure to accommodate transport by a gooseneck chassis. This feature is more common in forty foot and longer container
- 4.2 Walls, Roof, and Floor.
- 4.2.1 Fiberglass Reinforced Plywood (FRP).
A material constructed of laminates of fiberglass, polyester resins, and
plywood, also known as sandwich panel.
- 4.2.2 Wall Panel. Corrugated or flat sheet
steel, a riveted or bonded aluminum sheet and wall post assembly, FRP,
foam and beam, aluminum, or honeycomb material that forms the side wall or
end wall.
- 4.2.3 Wall Post. Interior or exterior
intermediate vertical component to which sheet aluminum or steel is
riveted or welded to form a wall panel.
- 4.2.4 Wall Beam. Encapsulated vertical
component to which sheet aluminum or steel is bonded to form a wall
panel.This is found in foam and beam panels.
- 4.2.5 Marking Panel. A side wall panel of
a corrugated steel configured with a flat portion used for the display of
markings and placards. (4.2A)
- 4.2.6 Lining. Plywood or other like
material attached to the interior side and end wall to protect the walls
and/or cargo and facilitate loading operations.
- 4.2.7 Lining Shield. A strip of thin metal
installed at the bottom of the interior walls to protect the lower portion
of the lining from damage by materials handling equipment during loading
or unloading operations.
- 4.2.8 Kick Plate. A common name for a
lining shield installed on the lower portion of the interior front end
wall.
- 4.2.9 Ventilator. Two or more devices
permanently attached to the side or end wall panel that provides openings
for the exchange of air (but not water) between the outside and the
container interior. (4.2A)
- 4.2.10 Roof Panel. Corrugated or flat
sheet steel, sheet aluminum, FRP, or foam and beam and aluminum honeycomb
panel that forms the top closure of the container. (4.2A,)
- 4.2.11 Roof Bow. Lateral non-structural
member attached to the top side rails and supporting the underside of the
roof panel. Roof bows used with removable cover (tarp) assembly are
unattached. Not all container designs require roof bows.
- 4.2.12 Roof Beam. Encapsulated horizontal
component to which sheet aluminum or steel is bonded to form a roof panel.
- 4.2.13 Roof Reinforcement Plate. An
additional metal plate on the interior or exterior of the roof panel
adjacent to the top corner fittings that provides protection of the roof
panel or top rail components from misaligned handling equipment.
- 4.2.14 Tarp. Jargon for
"tarpaulin" which is a waterproof and flexible fabric used for
covering the top of an open-top container. This covering is referred to as
a "Tilt" in some countries.
- 4.2.15 TIR Cable. Plastic sheathed wire
rope that is designed in accordance with TIR customs convention (Refer to
paragraph 4.5.6) and is threaded through the welded loops on the sides,
end panels and door panels of an open-top container to secure the tarp.
- 4.2.16 Flooring. Material that is
supported by the cross members and bottom rails to form a load bearing
surface for the cargo. The flooring is usually constructed of laminated
wood planks, plywood sheets, or other composition material and is screwed
or bolted to the cross members. Some containers have welded steel or
aluminum flooring, sandwhich panels or a combination of metal and wood.
(4.2A)
- 4.2.17 Joint Strip. A formed steel or
aluminum strip (usually hat-shaped section) installed between joints of
the plywood sheet flooring or joints of the plywood sheet lining to help
integrate and support the edges of the plywood. (4.2A)
- 4.2.18 Threshold plate. Plate forward of
the door sill to protect the entrance area of the container floor. This
plate is commonly referred to as a crash plate.
- 4.2.19 Steps. Folding steps are found on
some ISO Shelters and are used to gain access to the roof. They must be
folded up prior to transporting shelter.
- 4.2.20 Sandwich Panel. A type of fixed or
removable panel construction used in ISO Shelters consisting of a thin
inner and outer sheet aluminum skin, bonded or fastened to a core
constructed of either honeycomb or structural foam and aluminum beams.
- 4.2.21 Striker Plate. An additional metal
plate on the exterior of the roof panel adjacent to the top corner
fittings that provides protection to the roof panel or top rail components
from misaligned handling equipment.
- 4.2.22 Sling Pad. An additional metal plate on the exterior of the roof panel located in the center of the roof panel that provides protection to the panel from lowered handling equipment